PM (Polarization Maintaining) fiber is an essential component of fiber optic networks, providing high birefringence, low attenuation, and polarization maintenance. It is suited for fiber optic gyroscope (FOG) and polarization-sensitive component applications. This article is going to introduce PM fibers.
What is PM Fiber?
PM fiber is a specialty single-mode fiber that maintains linear polarization while the light propagates through the optical fiber. It is made through the high-precision PCVD (Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition) process. This process produces preforms with precise refractive index profiles, material uniformity, and dimensional tolerances. In addition, it provides high birefringence, low attenuation, excellent polarization-maintaining performance, dual-layer, UV-cured acrylate coating, high environmental stability, and reliability.
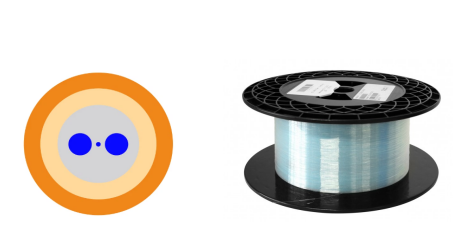
What Makes PM Fiber Maintain the Polarization?
In PM fiber, the fiber symmetry is broken by incorporating stress elements in the fiber cladding. The light is guide coupled in two perpendicular principle states of polarization with different propagation constants – the fast and the slow axis. The linear polarization of light coupled into one of these axes is maintained. The linearly polarized laser radiation is coupled into the slow axis because of its lower sensitivity to fiber bending. If the light is coupled into both axes then the resulting polarization is elliptical strain and temperature variations, changing this arbitrary elliptical state.

What is the Working Principle of PM Fiber?
PM fiber works by intentionally inducing linear birefringence in the fiber so that two polarization modes propagate along the entire fiber length with very distinct phase velocities. In addition, it prohibits random power coupling between two polarization modes. The propagation constants of the two polarization modes are different due to the strong birefringence. This leads to a rapid drift away from the relative phase of such a co-propagating mode. If this difference is large enough, the usual disturbances in the fiber are too slowly varying to do effective mode coupling.
Different Types of PM Fibers
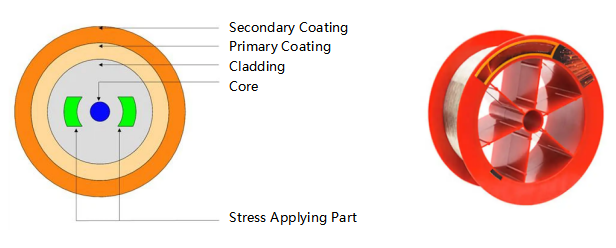
1) PANDA PM Fiber
PANDA PM fiber provides low attenuation and excellent birefringence for high-performance applications. Its design uses two stress-applying parts to create an extremely high birefringence, resulting in fiber with excellent PM properties.
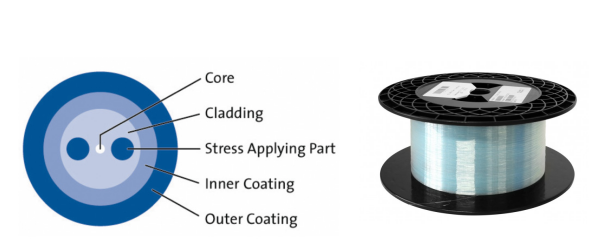
2) Bow-Tie PM Fiber
Bow-tie PM fiber or highly birefringent (HiBi) fiber uses bow-tie stress-applying-part (SAP) to create birefringence in the core. It provides less beat length and high birefringence without excessive stress, allowing polarization orientation to be controlled effectively across a fiber system.
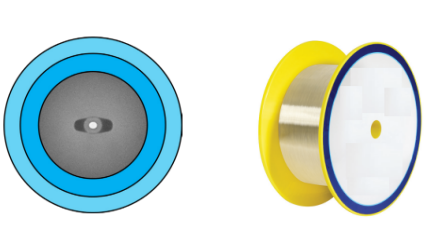
3) Elliptical Core PM Fiber
The elliptical core PM fiber has high birefringence and bending performance, low loss, excellent temperature stability, good geometric uniformity, and polarization-maintaining performance.
4) Elliptical Clad PM Fiber
Elliptical-clad PM fiber is based on elliptical-clad stress technology. It provides high birefringence, short beat length, excellent for high-precision gyroscopes, and low attenuation than other PM fiber types.
Applications
PM fiber is used in interferometry, fiber optic laser, LED source, fiber optic sensing, quantum key distribution, planar waveguide, coherent optical transmission, FOG, polarization-sensitive components, optical fiber coupling, splitter, fused-fiber coupler, patch cord, pigtail, etc.
Conclusion
PM fiber is the ideal solution for polarization-sensitive components applications to provide high birefringence, high environmental stability and reliability, and low attenuation. It is suitable for the transmission of light with operating wavelengths of 1300 nm or 1550 nm.
Sun Telecom specializes in providing one-stop total fiber optic solutions for all fiber optic application industries worldwide. Contact us if you have any needs.
Questions
1. What is PM Fiber?
2. What are the Applications of PM Fiber?
3. What are the Benefits of Using PM Fiber?
4. How Does the PM Fiber Work?
5. How Many Types of PM Fibers are Available in the Market?


 Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products
Position :
Home>
News & Tutorial
>Products





 Position :
Home
>Products
Position :
Home
>Products




 ics@suntelecom.cn
ics@suntelecom.cn  +86 18964888554
+86 18964888554 Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China
Building No.145, Lane 666 Xianing Road, Jinshan Industrial Zone, Shanghai 201506, China